Lessons learned from the 2025 7th Grade Math STAAR
- Aaron Daffern
- Dec 26, 2025
- 6 min read
Using a modified version of the statewide item analysis report, I examined the readiness standards that had less than 60% mastery. Each standard has both an analysis of the items themselves to infer what made them so difficult and instructional implications for educators to ensure a more successful 2026 STAAR test.
Standard | # of items | % mastery |
7.3B | 2 | 38 |
7.9C | 2 | 38.5 |
7.4D | 2 | 42 |
7.11A | 2 | 44 |
7.6G | 2 | 44.5 |
7.9A | 2 | 44.5 |
7.6I | 2 | 46.5 |
7.7A | 2 | 46.5 |
7.5C | 2 | 48 |
7.9B | 2 | 49.5 |
7.4A | 2 | 55.5 |
7.12A | 2 | 57.5 |
Access the slide deck here.
7.3B - 38% overall mastery
apply and extend previous understandings of operations to solve problems using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of rational numbers
#11 - 27% correct

#36 - 49% correct

Analysis
Instructional Implications
Both problems involved mixed numbers/fractions, reinforcing need for students to be comfortable changing between fractions and decimals
Surprisingly, students did much better on the word problem (#36) with the hidden operation of multiplication (i.e., discount)
7.9C - 38.5% overall mastery
determine the area of composite figures containing combinations of rectangles, squares, parallelograms, trapezoids, triangles, semicircles, and quarter circles
#12 - 27% correct

#22 - 50% correct

Analysis
Instructional Implications
Encourage students to look for simpler problems (e.g., make a new shape by rearranging the existing shapes)
Practice should emphasize finding missing side lengths using deduction
Watch the full walkthrough of all 38 items on the 2025 7th Grade STAAR below.
7.4D - 42% overall mastery
solve problems involving ratios, rates, and percents, including multi-step problems involving percent increase and percent decrease, and financial literacy problems
#7 - 33% correct

#38 - 51% correct

Analysis
Instructional Implications
Recognition of the type of problem (percent increase/decrease vs ratio/rate) is the first step in solving these types of problems
If the latter, students need time and practice to recognize when to solve for a unit rate (if needed) and when to set up a proportion
7.11A - 41% overall mastery
model and solve one-variable, two-step equations and inequalities
#16 - 37% correct

#33 - 51% correct

Analysis
Instructional Implications
The two largest challenges with inequalities and verbal descriptions are:
Identifying the correct symbol from the context of the word problem
Flipping the inequality when multiplying or dividing by a negative
Have students work out some of the x- and y-values for word problems and then plug them back in to check their work
7.6G - 42% overall mastery
solve problems using data represented in bar graphs, dot plots, and circle graphs, including part-to-whole and part-to-part comparisons and equivalents
#15 - 36% correct

#30 - 53% correct

Analysis
Instructional Implications
By 7th grade, students’ work with graphs will come down to finding the percent or fraction the amounts shown
By turning each statement to evaluate (#15) into a number sentence, students can more easily evaluate them
7.9A - 44.5% overall mastery
solve problems involving the volume of rectangular prisms, triangular prisms, rectangular pyramids, and triangular pyramids
#5 - 36% correct

#26 - 53% correct

Analysis
Instructional Implications
These calculations require basic use of formula
Work with students to use the commutative property of multiplication to make simpler problems first
7.6I - 46.5% overall mastery
determine experimental and theoretical probabilities related to simple and compound events using data and sample spaces
#13 - 60% correct

#24 - 33% correct

Analysis
Instructional Implications
The first step in solving probability is to classify the problem as a simple or compound event
Students should have practice with compound events with the same and different denominators
7.7A - 46.5% overall mastery
represent linear relationships using verbal descriptions, tables, graphs, and equations that simplify to the form y = mx + b
#9 - 63% correct

#21 - 11% full credit; 35% partial credit; 54% no credit

Drop-down 1: -3; -2; 3; 5
Drop-down 2: -4; 0; 3; 5
Analysis
Instructional Implications
Identifying key features is still a struggle for students in Algebra I and get more challenging as x-intercepts (i.e., zeros, solutions) are introduced later
Show students how to calculate slope when given a graph without using the slope formula (rise/run)
7.5C - 48% overall mastery
solve mathematical and real-world problems involving similar shape and scale drawings
#10 - 41% correct

#20 - 55% correct

Analysis
Instructional Implications
Emphasize labeling units when setting up proportions
Have students use reasoning to eliminate answer choices
7.9B - 49.5% overall mastery
determine the circumference and area of circles
#8 - 21% full credit; 36% partial credit; 43% no credit

#29 - 60% correct

Analysis
Instructional Implications
The relationship between radius and diameter can be derived from the formulas for circumference
C = πd
C = 2πr
Since students had to calculate without technology and the answer choices did not include decimals, estimation would have been appropriate
7.4A - 55.5% overall mastery
represent constant rates of change in mathematical and real-world problems given pictorial, tabular, verbal, numeric, graphical, and algebraic representations, including d = rt
#4 - 64% correct

#31 - 47% correct

Analysis
Instructional Implications
The initial step is to recognize problem situations that describe a constant rate of change
Students should be comfortable multiplying and dividing by multiples of 10, 100, or 1,000
7.12A - 57.5% overall mastery
compare two groups of numeric data using comparative dot plots or box plots by comparing their shapes, centers, and spreads
#17 - 55% correct

#34 - 39% full credit; 42% partial credit; 19% no credit
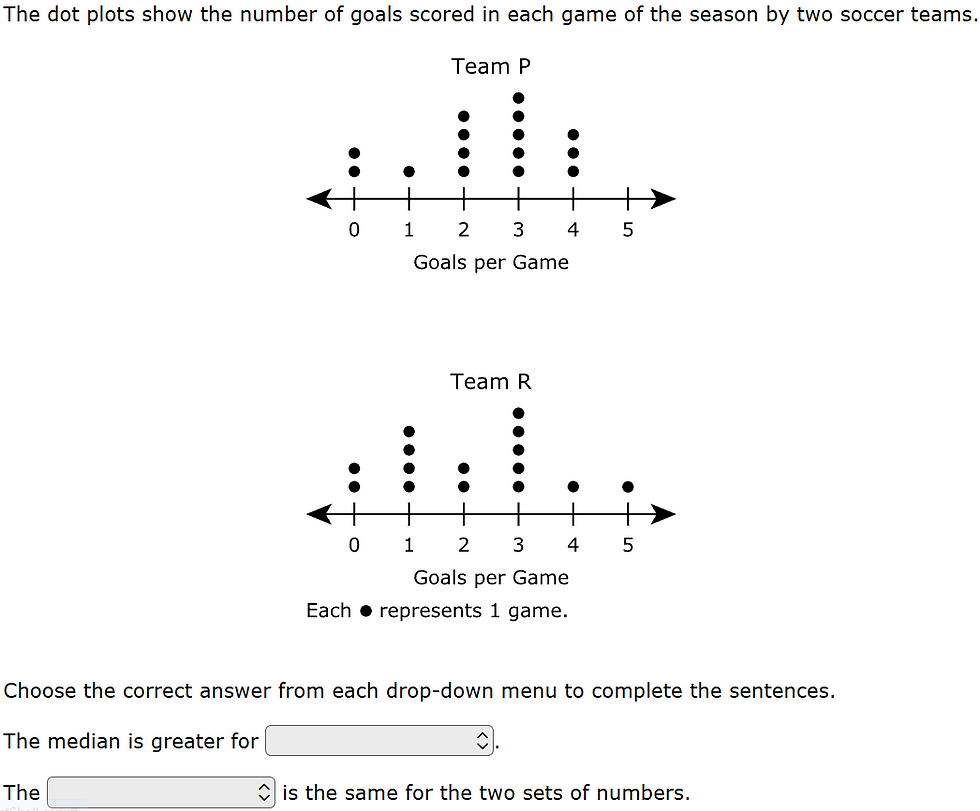
Drop-down 1: team P; team R
Drop-down 2: mode; range; maximum
Analysis
Instructional Implications
Students should be well-versed in measures of center (median, mean), measures of spread (range, IQR), and the shape (e.g., symmetry) of data representations
As stated in the TEKS, this standard is about comparing two sets of data


Comments